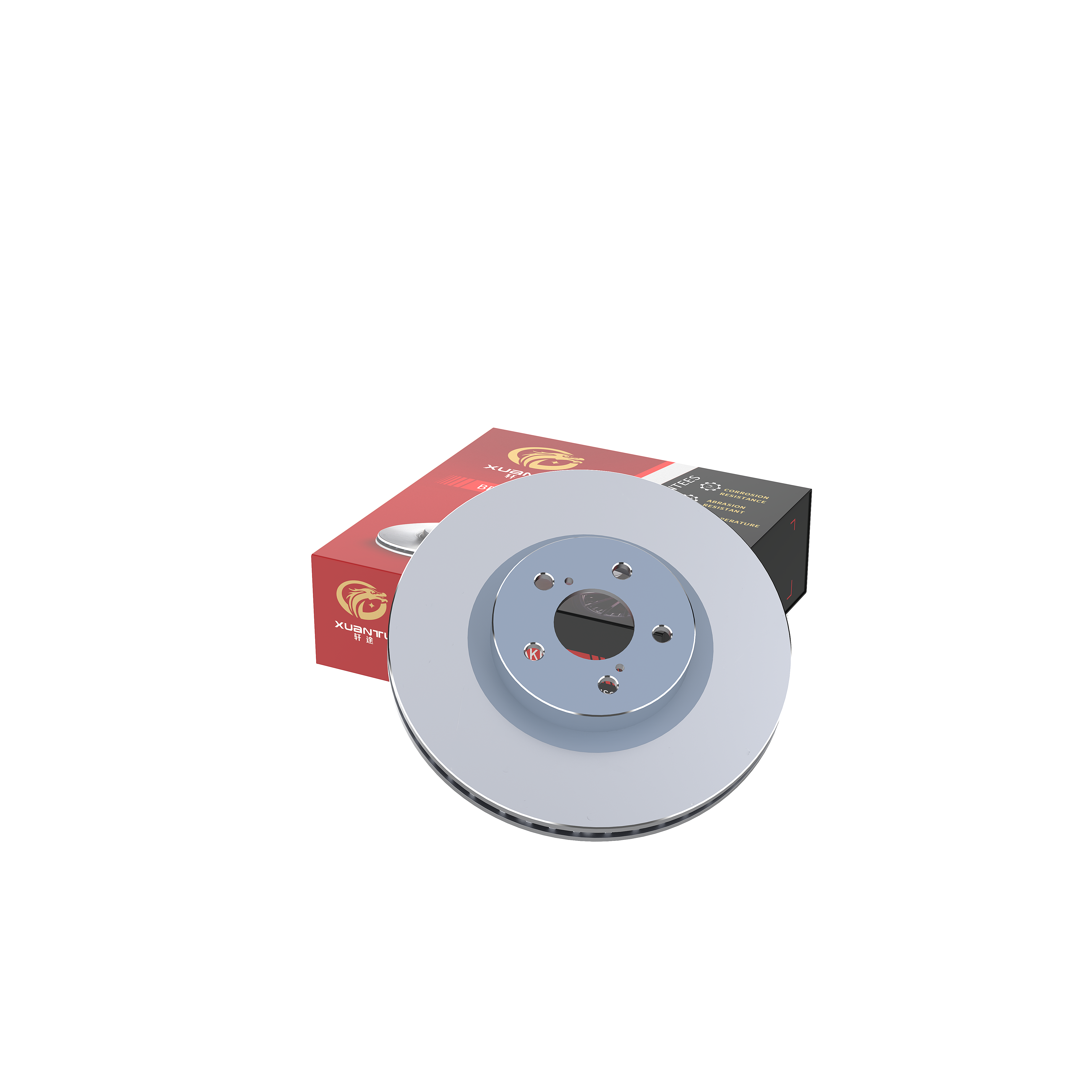
disc brake
A disc brake represents a sophisticated braking mechanism widely employed in modern vehicles and machinery. This system consists of a metal disc, or rotor, attached to the wheel or axle, and a caliper assembly that houses the brake pads. When the brake pedal is engaged, hydraulic pressure forces the brake pads to clamp against both sides of the rotating disc, creating friction that effectively slows or stops the vehicle. The disc brake's design incorporates advanced materials and engineering principles to ensure reliable performance across various operating conditions. Key components include the ventilated rotors that facilitate heat dissipation, high-friction brake pads manufactured from composite materials, and precision-engineered calipers that ensure even pressure distribution. This braking system finds extensive applications in automobiles, motorcycles, bicycles, and industrial equipment, offering superior stopping power and control. The technology has evolved to include features such as anti-lock braking systems (ABS), electronic brake force distribution, and brake assist systems, making it an integral part of modern vehicle safety systems. Disc brakes operate effectively in diverse weather conditions and maintain consistent performance levels even during extended use, making them the preferred choice for both everyday transportation and high-performance applications.